
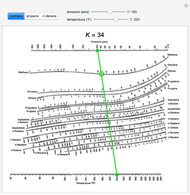
Definition of relative volatility: alpha (i/j)=K (i)/K (j), where K=y/x, where y is the vapor composition and x is the liquid composition. … (2) We can use K-values directly, by looking values up (DePriester Charts) or using correlations. The equilibrium curve y versus x for n-pentane and n-hexane An equilibrium line describes the compositions of the liquid and vapor in equilibrium at a fixed pressure. The Fenske equation was also used to estimate the minimum number of theoretical plates neces sary to obtain 99% pure (agent-free basis) products. Open up your existing Aspen simulation and click on the Separators tab in the Equipment Model Library. Aspen Distillation Options: Aspen has multiple unit operations options for completing distillation problems, based on the complexity of the user’s application. appears and the relative volatility adequately alters. € α LK = K LK K HK, α i = K i K HK (6.1) Then, use the Fenske equation (Fenske, 1932). = relative volatility between the two components on stage k. After that i will need a stripper to seperate amin and H 2 S but i couldnt find relative volatility for these too. I dont know Yi and Xi values so im looking for a different way to calculate K. 1) Relative volatility at saturated feed condition.
#Ethylene glycol depriester chart plus#
to buy when RVI readings move above 50 (RVI values become green after been green in the last column in the table below) to sell when RVI drops below 50 (RVI values become red after been green in the last column in the table … Although you have Aspen Plus to do the calculations, it is instructive to see what equations are being used. Mole fraction of each hydrocarbon in lean oil. Implied volatility is a calculation that uses an option’s Vega (its sensitivity to change in volatility) to derive an estimate of volatility. v i = option’s Vega at theoretical value y i.
y i = option’s theoretical value at volatility x i. Another method can be using the basic equation of relative volatility= ((Ya/Xa)/ (Yb/Xb))=Ka/Kb.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
